Google Scholar | PubMed | Research Gate
The documents distributed here have been provided as a means to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work on a noncommercial basis. Copyright and all rights therein are maintained by the authors or by other copyright holders, notwithstanding that they have offered their works here electronically. It is understood that all persons copying this information will adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each author’s copyright. These works may not be reposted without the explicit permission of the copyright holder.
Submitted / In Press
Schmälzle, R. & Lim, S. (Submitted / In Press). A neuroscientific window into the audience brain: Capturing how rhetoric creates resonance. The Forensic of Pi Kappa Delta.
2026
Lim, S., Schmälzle, R., & Bente, G. (2026). Examining speakers’ subjective and bio-behavioral responses to audience-induced social-evaluative threat via immersive VR. Scientific Reports. [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Cho, H. J., & Turner, M. (2026). The Signal in the Noise: Hierarchy and Robustness of Physiological Audience Alignment during Narrative Media. biorxiv. [PDF] [Code]
Jeon, M., Lim, S., Lapinski, M., Spates, S., Bente, G., & Schmälzle, R. (2026). Visual attention and retention effects of a design element in culturally targeted messages: Introducing the Virtual Billboard Paradigm. Communication Quarterly, 1-31. [PDF] [Code]
2025
Pena, J., Huskey, R., Gong, X., Andrews, M., Weisman, W., Kee, R., Klein, V., Sarieva S, K. R., Schmälzle, R., & Hancock, J. (2025). Media Neuroscience on a shoestring 2.0: Using AR and mobile EEG hyperscanning to study cooperation. Journal of Media Psychology. [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Lim, S., Du, Y., & Bente, G. (2025). The art of audience engagement: LLM-based thin-slicing of scientific talks. arXiv. [PDF] [Code]
Huskey, R. & Schmälzle, R. (2025). Finding middle ground In cognitive media psychology. In. N. Bowman & N.D. Shackleford (Eds). Oxford Handbook of Media Psychology, 1.
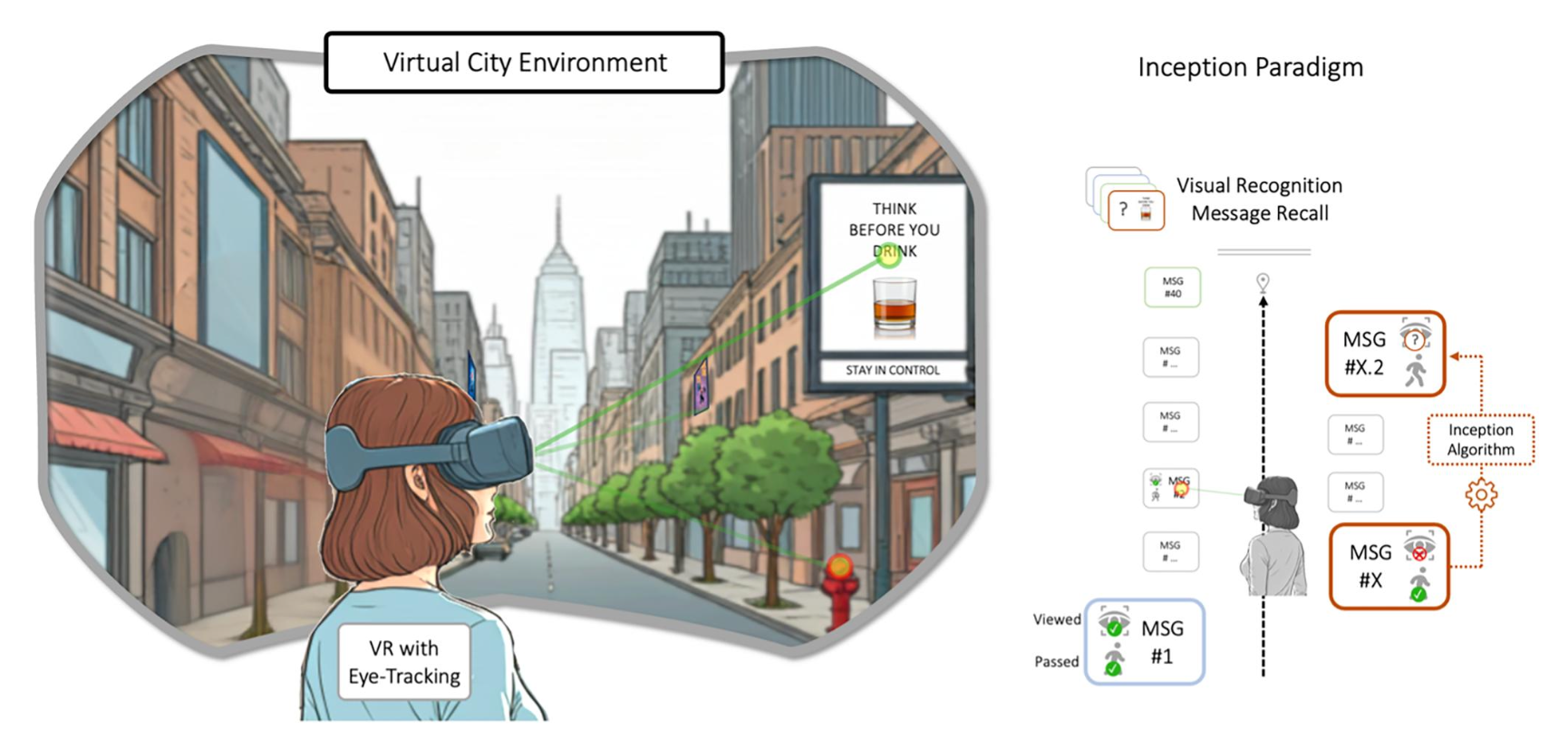
Cho, H. J., Lim, S., Saenz, M., & Schmälzle, R. (2025). Memory inception through gaze-contingent message exposure: Using Virtual Reality to study media influence. Journal of Communication. [Code]
Hussain, A., Schmälzle, R., Lim, S., & Bouali, N. (2025). Comparing AI and human-generated health messages in an Arabic cultural context. Global Health Action, 18(1), 2464360. [PDF] [Code]
Lim, S., Schmälzle, R., & Bente, G. (2025). Artificial social influence via human-embodied AI agent interaction in immersive virtual reality (VR): Effects of similarity-matching during health conversations. Computers in Human Behavior Artificial Humans, 5, 100172. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R. & Lim, S. (2025). From blank page to campaign plan: Using the CampAIgner AI tool to scaffold public communication campaign design. Communication Teacher. [PDF] [Code]
Lim, S., Schmälzle, R., & Bente, G. (2025). A VR-based paradigm for examining relationship-building behaviors in LLM-driven intelligent virtual agents (IVAs). Designing and Evaluating Behavioural Paradigms With Proactive Virtual Agents (DEBP-PVA) @ 25th ACM International Conference on Intelligent Virtual Agents (IVA).
Lim, S., Schmälzle, R., & Bente, G. (2025). Artificial social influence: Rapport-building, LLM-based embodied conversational agents for health coaching. Connect @ 24h ACM International Conference on Intelligent Virtual Agents (IVA). [PDF]
Schmälzle, R., Lim, S., Du, Y., & Bente, G. (2025). The art of audience engagement: LLM-based thin-slicing of scientific talks. Frontiers in Communication, 10, 1610404. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Wu, J., Lim, S., & Bente, G. (2025). Inter-subject correlations of pupillary audience responses: Decoding visual attention and predicting memory in a VR media setting. Journal of Media Psychology. [Code]
Bente, G., Schmälzle, R., Jahn, N. T., & Reimers, M. (2025). Reading the Social Clock. Analyzing Nonverbal Coordination Dynamics in Casual Chat and Conflict. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R., Wilcox, S., & Huskey, R. (2025). Brain imaging as a window into the biological basis of social cognition and communication. In. T. Reimer and L. van Swol, Lyn and A. Florack (Eds.). Handbook of Communication and Social Cognition.
Cho, H. J., Lim, S., Turner, M., Bente, G., & Schmälzle, R. (2025). Eyes on VR: Unpacking the causal chain between exposure, reception, and retention for emotional billboard messages. Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies, 1, 3619411. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R. (2025). Eye Tracking (Eye Tracking in Political Education Campaigns). PRIF (Peace Research Institute Frankfurt) Reports.
Cho, H. J., Lim, S., Saenz, M., & Schmälzle, R. (2025). Memory inception through gaze-contingent message exposure: Using Virtual Reality to study media influence. bioRxiv. [PDF] [Code]
Cho, H. J., Lim, S., Saenz, M., & Schmälzle, R. (2025). Memory inception through gaze-contingent message exposure: Using Virtual Reality to study media influence. Journal of Communication. [Code]
Lim, S., Schmälzle, R., & Bente, G. (2025). Speaker responses to audience-induced social-evaluative threat: Evidence from scientific presentation tasks in immersive virtual reality. biorxiv. [PDF] [Code]
2024
Schmälzle, R., Lim, S., Jahn, N., Wilcox, S., & Ye, Q. (2024). Collective brain alignment during story reception: Shared neural responses in French, Chinese, and English listeners of Le Petit Prince (The Little Prince). Asian Communication Research, 21(3), 195-217. [PDF] [Code]
Lim, S. & Schmälzle, R. (2024). Exploring the mechanisms of AI message generation: A chatbot development activity for students. Communication Teacher, 38(1), 21-27. [PDF] [Code]
Tamborini, R., Schmälzle, R., & Bowman, N. D. (2024). The role of theory in media entertainment research. In. N. Bowman (Eds). DeGryuter Handbook of Entertainment Media and Communication, 1.
Imhof, M. A., Flösch, K. P., Schmälzle, R., Renner, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2024). Portable EEG in groups shows increased brain coupling to strong health messages. Social, Cognitive, and Affective Neuroscience, 19(1), nsae087. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R., Lim, S., Bezbaruah, S., Wu, J., & Hussain, S. A. (2024). Converging crowds and tied twins: Audience brain responses to the same movie are consistent across continents and enhanced among twins. Journal of Media Psychology, 37(3), 144-157. [PDF] [Code]
Lim, S. & Schmälzle, R. (2024). The effect of source disclosure on evaluation of AI-generated messages: A two-part study. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans, 2(1), 100058. [PDF] [Code]
Lim, S., Cho, H., Jeon, M., Cui, X., & Schmälzle, R. (2024). Using VR and eye-tracking to study attention to and retention of AI-generated ads in outdoor advertising environments. bioRxiv. [PDF] [Code]
Jeon, M., Lim, S., Lapinski, M., Spates, S., Bente, G., & Schmälzle, R. (2024). Attention and retention effects of culturally targeted billboard messages: An eye-tracking study using immersive Virtual Reality. bioRxiv. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Jahn, N., & Bente, G. (2024). Charting the silent signals of social gaze: Automating eye contact assessment in face-to-face conversations. bioRxiv. [PDF] [Code]
Cho, H. J., Lim, S., Turner, M., Bente, G., & Schmälzle, R. (2024). Eyes on VR: Unpacking the causal chain between exposure, reception, and retention for emotional billboard messages. bioRxiv. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Wu, J., Lim, S., & Bente, G. (2024). The eyes have it: Inter-subject correlations of pupillary responses for audience response measurement in VR. bioRxiv. [PDF] [Code]
2023
Holmstrom, A., Dorrance-Hall, E., Wilcox, S., & Schmälzle, R. (2023). Confirmation, disconfirmation, and communal coping for joint physical activity in romantic dyads. Health Communication, 39(6), 1067-1081. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R. & Huskey, R. (2023). Integrating media content analysis, reception analysis, and media effects studies. Frontiers in Neuroscience (Neuroscience and the Media), 17, 1155750. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R., Liu, H., Delle, F., Lewin, K., Jahn, N. T., Zhang, Y., Yoon, H., & Long, J. (2023). Moment-by-moment tracking of audience brain responses to an engaging public speech: Replicating the reverse-message engineering approach. Communication Monographs, 91(1), 31-55. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R. & Huskey, R. (2023). Skyhooks, cranes, and the construct dump: A comment on and extension of Boster (2023). Asian Communication Research, 20(2), 84-94. [PDF]
Lim, S. & Schmälzle, R. (2023). The effect of source disclosure on evaluation of AI-generated messages: A two-part study. arXiv. [PDF]
Lim, S. & Schmälzle, R. (2023). Artificial intelligence for health message generation: an empirical study using a large language model (LLM) and prompt engineering. Frontiers in Communication, 8, 1129082. [PDF] [Code]
Bente, G., Schmälzle, R., Jahn, N., & Schaaf, A. (2023). Measuring the effects of co-location on emotion perception in shared virtual environments: An ecological perspective. Frontiers in Virtual Reality, 9, 449. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Lim, S., Cho, H. J., Wu, J., & Bente, G. (2023). Examining the exposure-reception-retention link in realistic communication environments via VR and eye-tracking: The VR billboard paradigm. PlosOne, 18(11), e0291924. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Lim, S., Cho, H. J., Wu, J., & Bente, G. (2023). The VR billboard paradigm: Using VR and eye-tracking to examine the exposure-reception-retention link in realistic communication environments. bioRxiv. [PDF] [Code]
2022
Lim, S. & Schmälzle, R. (2022). Artificial intelligence for health message generation: An empirical study using a large language model (LLM) and prompt engineering. arXiv, 2212.07507. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R. (2022). Theory and method for studying how messages prompt shared brain responses along the sensation-to-cognition continuum. Communication Theory, 32(4), 450-460. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R. & Wilcox, S. (2022). Harnessing artificial intelligence for health message generation: The folic acid message engine. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 22(1), e28858. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Wilcox, S., & Jahn, N. T. (2022). Identifying moments of peak audience engagement from brain responses during story listening. Communication Monographs, 89(4), 515-538. [PDF] [Code]
Jahn, N., Bente, G., Meshi, D., & Schmälzle, R. (2022). Media neuroscience on a shoestring: Examining electrocortical responses to visual stimuli via mobile EEG. Journal of Media Psychology, 35(2), 75-86. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Grady, S. M., & Baldwin, J. A. (2022). Examining the relationship between story structure and audience response: How shared brain activity varies over the course of a narrative. Projections – Journal for Movies and Mind, 16(3), 1-28. [PDF] [Code]
Bente, G., Schmälzle, R., Kryston, K., & Jahn, N. (2022). Building blocks of suspense. Subjective and physiological effects of narrative content and film music. Nature Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 9, 449. [PDF] [Code]
2021
Anderson, J., Lapinski, M., Turner, M., Peng, T., & Schmälzle, R. (2021). Speaking of values: Value-expressive communication and exercise intentions. Health Communication, 37(10), 1285-1294. [PDF]
Grall, C., Weber, R., Tamborini, R., & Schmälzle, R. (2021). Stories collectively engage listeners’ brains: Enhanced intersubject correlations during reception of personal narratives. Journal of Communication, 71(2), 332-355. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Wilcox, S., & Grall, C. (2021). Neuroimaging in environmental communication research. In. Takahashi, B. Metag, J. Thaker, J. & Evans-Comfort, S.: ICA-Routledge Handbook of International Trends in Environmental Communication, 437-448. [PDF]
Baldwin, J. A. & Schmälzle, R. (2021). A character recognition tool for automatic detection of social characters in visual media content. Computational Communication Research, 4(1). [PDF] [Code]
Dorrance-Hall, E., Wilcox, S., Holmstrom, A., McGraw, J., & Schmälzle, R. (2021). Reactance to healthy eating and physical activity messages: Face threat and face management strategies in memorable daily conversations among couples. Health Communication, 38(7), 1404-1415. [PDF]
2020
Grall, C. & Schmälzle, R. (2020). Neurocinematics. In. J. VanDenBulck & M.-L. Mares: The International Encyclopedia of Media Psychology. [PDF]
Huskey, R., Eden, A., Grall, C., Meshi, D., Prena, K., Schmälzle, R., Scholz, C., Turner, B., & Wilcox, S. (2020). Marr’s tri-level framework integrates biology with communication science. Journal of Communication, 70, 356-378. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R. & Grall, C. (2020). Mediated messages and synchronized brains. In. Floyd & Weber: Handbook of Communication Science and Biology, 109-122. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R. & Grall, C. (2020). Psychophysiological methods: Options, uses, and validity. In. J. VanDenBulck & M.-L. Mares: The International Encyclopedia of Media Psychology. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R., Cooper, N., O’Donnell, M. B., Tompson, S., Lee, S., Cantrell, J., Vettel, J. M., & Falk, E. B. (2020). The effectiveness of online messages for promoting smoking cessation resources: Predicting nationwide campaign effects from neural responses in the EX campaign. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 14 [Shared frist authorship]. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R. & Grall, C. (2020). The coupled brains of captivated audiences: An investigation of the collective brain dynamics of an audience watching a suspenseful film. Journal of Media Psychology, 1-13 [Shared frist authorship]. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R. & Meshi, D. (2020). Communication neuroscience: Theory, methodology, and experimental approaches. Communication Methods and Measures, 1(1), 1-16 [Shared first authorship]. [PDF]
Imhof, M. A., Schmälzle, R., Renner, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2020). Strong health messages increase audience brain coupling. NeuroImage, 216, 116527. [PDF] [Code]
Wilcox, S., Dorrance-Hall, E., Homstrom, A., & Schmälzle, R. (2020). The emerging frontier of interpersonal communication and neuroscience: Scanning the social synapse. Annals of the International Communication Association, 44(4), 368-384. [PDF]
2019
Kranzler, E. C., Schmälzle, R., O’Donnell, M. B., Pei, R., & Falk, E. B. (2019). Adolescent neural responses to antismoking messages, perceived effectiveness, and sharing intention. Media Psychology, 22(2), 323–349. [PDF] [Code]
Kranzler, E. C., Schmälzle, R., O’Donnell, M. B., Pei, R., & Falk, E. B. (2019). Message-elicited brain response moderates the relationship between opportunities for exposure to anti-smoking messages and message recall. Journal of Communication, 69(5), 589-611. [PDF]
Pei, R., Schmälzle, R., Kranzler, E. C., O’Donnell, M. B., & Falk, E. B. (2019). Adolescents’ neural response to tobacco prevention messages and sharing engagement. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 56(2S1), S40–S48. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R., Hartung, F., Barth, A., Imhof, M. A., Kenter, A., Renner, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2019). Visual cues that predict intuitive risk perception in the case of HIV. PLoS One, 14(2), e0211770. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Imhof, M. A., Kenter, A., Renner, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2019). Impressions of HIV risk online: Brain potentials while viewing online dating profiles. Cognitive, Affective and Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(2), e1. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Imhof, M. A., Kenter, A., Renner, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2019). Impressions of HIV risk online: Brain potentials while viewing online dating profiles. Cognitive, Affective and Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(2), e1. [Code]
2018
Kryston, K., Novotny, E., Schmälzle, R., & Tamborini, R. (2018). Video games: A medium that demands our attention. [PDF]
Schlicht-Schmälzle, R., Chykina, V., & Schmälzle, R. (2018). An attitude network analysis of post-national citizenship identities. PLoS One, 13(12), e0208241. [PDF] [Code]
2017
Imhof, M. A., Schmälzle, R., Renner, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2017). How real-life health messages engage our brains: Shared processing of effective anti-alcohol videos. Social, Cognitive, and Affective Neuroscience, 12(7), 1188-1196 [Shared first authorship]. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R., Brook O’Donnell, M., Garcia, J. O., Cascio, C. N., Bayer, J., Vettel, J., Bassett, D., & Falk, E. B. (2017). Brain connectivity dynamics during social interaction reflect social network structure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(20), 5153-5158. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Imhof, M. A., Grall, C., Flaisch, T., & Schupp, H. T. (2017). Reliability of fMRI time series: Similarity of neural processing during movie viewing. biorxiv. [PDF] [Code]
Schmälzle, R., Renner, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2017). Health risk perception and risk communication. Policy Insights from the Behavioral and Brain Sciences. [PDF]
2016
Schupp, H. T., Kirmse, U., Schmälzle, R., Flaisch, T., & Renner, B. (2016). Newly-formed emotional memories guide selective attention processes: Evidence from event-related potentials. Scientific Reports, 6, 28091. [PDF]
2015
Barth, A., Schmälzle, R., Hartung, F., Britta Renner, & Schupp, H. T. (2015). How target and perceiver gender affect impressions of HIV risk. Frontiers in Public Health, section HIV and AIDS, 3(1), 223. [PDF]
Becker, C., Schmälzle, R., Flaisch, T., & Schupp, H. T. (2015). Thirst and the state-dependent representation of incentive stimulus value in human motive circuitry. Social, Cognitive, and Affective Neurosciences, 10(12), 1722-1729. [PDF]
Flaisch, T., Imhof, M., Schmälzle, R., Wentz, K., Ibach, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2015). Implicit and explicit attention to pictures and words: An fMRI-study of concurrent emotional stimulus processing. Frontiers in Psychology, 6(1), 1861. [PDF]
Renner, B., Gamp, M., Schmälzle, R., & Schupp, H. T. (2015). Health risk perception. International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 10, 702-709. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R., Häcker, F., Honey, C. J., & Hasson, U. (2015). Engaged listeners: Shared neural processing of powerful political speeches. Social, Cognitive, and Affective Neurosciences, 1, 168-169. [PDF]
2014
Häcker, F., Schmälzle, R., Renner, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2014). Neural correlates of HIV risk feelings. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, doi:10.1093/scan/nsu093(nsu093), 1-6. [PDF]
Schupp, H. T., Schmälzle, R., & Flaisch, T. (2014). Explicit semantic stimulus categorization interferes with implicit emotion processing. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 9, 1738–1745. [PDF]
2013
Schmälzle, R., Häcker, F., Renner, B., Honey, C. J., & Schupp, H. T. (2013). Neural correlates of risk perception during real-life risk communication. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(25), 10340–10347. [PDF]
Barth, A., Schmälzle, R., Renner, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2013). Neural correlates of risk perception: HIV vs. leukemia. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 7(1), 1. [PDF]
2012
Renner, B., Schmälzle, R., & Schupp, H. T. (2012). First impressions of HIV risk: it takes only milliseconds to scan a stranger. PloS One, 7(1), e30460. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R., Renner, B., & Schupp, H. T. (2012). Neural correlates of perceived risk: the case of HIV. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 7(6), 667–676. [PDF]
Schupp, H. T., Schmälzle, R., Flaisch, T., Weike, A. I., & Hamm, A. O. (2012). Affective picture processing as a function of preceding picture valence: An ERP analysis. Biological Psychology, 91(1), 81-87. [PDF]
2011
Schmälzle, R., Schupp, H. T., Barth, A., & Renner, B. (2011). Implicit and explicit processes in risk perception: neural antecedents of perceived HIV risk. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 5(1), 1. [PDF]
2010
Bublatzky, F., Flaisch, T., Stockburger, J., Schmälzle, R., & Schupp, H. T. (2010). The interaction of anticipatory anxiety and emotional picture processing: An event-related brain potential study. Psychophysiology, 47(4), 687–696. [PDF]
2009
Renner, B., Schupp, H. T., & Schmälzle, R. (2009). Risikowahrnehmung und Risikokommunikation. Handbuch ü Gesundheitspsychologie und Medizinische Psychologie, 16(3), 113–121. [PDF]
Schmälzle, R. (2009). Intuitive risk perception: A neuroscientific approach. PhD thesis, –, -. [PDF]
Stockburger, J., Schmälzle, R., Flaisch, T., Bublatzky, F., & Schupp, H. T. (2009). The impact of hunger on food cue processing: an event-related brain potential study. Neuroimage, 47(4), 1819–1829. [PDF]
2008
Renner, B., Schupp, H., Vollmann, M., Hartung, F., Schmälzle, R., & Panzer, M. (2008). Risk perception, risk communication and health behavior change. Zeitschrift für Gesundheitspsychologie, 16(3), 150–153. [PDF]
Schupp, H. T., Stockburger, J., Schmälzle, R., Bublatzky, F., Weike, A. I., & Hamm, A. O. (2008). Visual noise effects on emotion perception: brain potentials and stimulus identification. Neuroreport, 19(2), 167–171. [PDF]